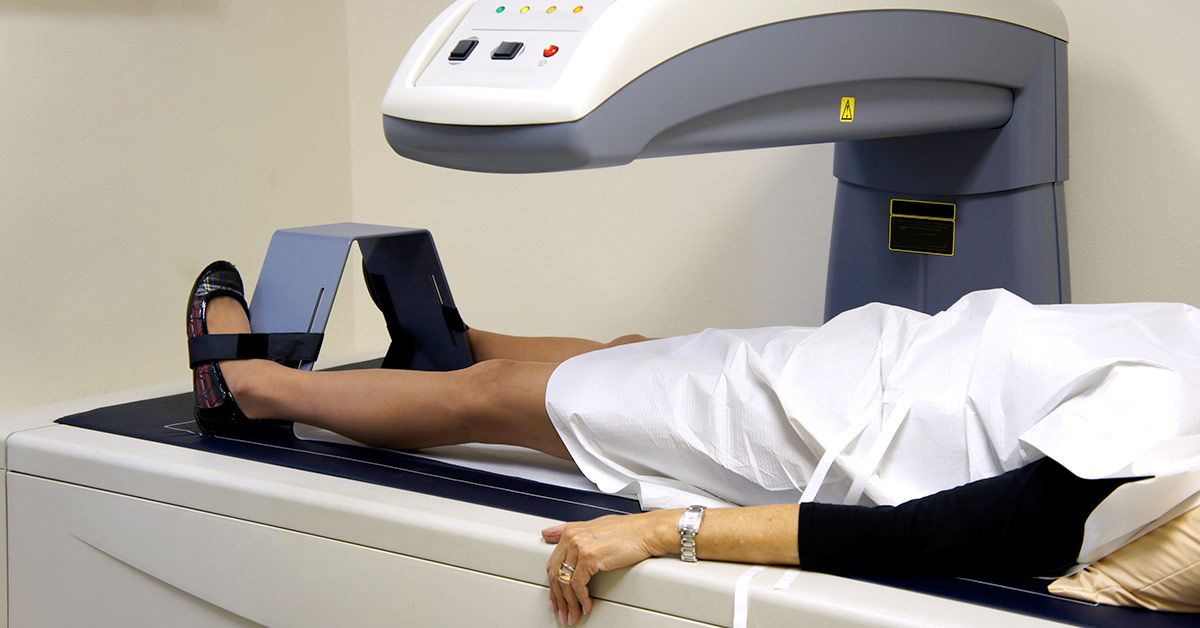
What is it?
- Bone Density scanning, also called Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) or Bone Densitometry, is an enhanced form of X-Ray technology that is used to measure bone mineral content and observe if any bone loss progression has gone on.
- A bone mineral density (BMD) test measures calcium and other minerals in bone.
- Bones containing more minerals are denser, so they tend to be stronger and less likely to break. Bones can become less dense as we age or if we develop certain medical conditions. When too much bone is lost, osteoporosis can develop.
- DXA is today’s established standard for measuring Bone Mineral Density (BMD).
Risks?
Bone density scans are quite safe. They use minimal levels of radiation than that of a standard X-ray.
Ontario Health recommends that all patients over 50 years of age have a baseline test. Based on the results of this test, and your medical history, the radiologist and your health care provider will determine when your follow up exam will be.
A T score of -1 to +1 is considered normal bone density. A T score of -1 to -2.5 indicates osteopenia (low bone density). A T score of -2.5 or lower is bone density low enough to be categorized as osteoporosis.
Bone density testing is strongly recommended if you:
· Have experienced a fracture after only mild trauma.
· Have had x-ray evidence of vertebral fracture or other signs of osteoporosis.
· Are a postmenopausal female and not taking estrogen.
· Have a personal or maternal history of hip fracture or smoking.
· Are a male with clinical conditions associated with bone loss.
· Use medications that are known to cause bone loss, including corticosteroids such as Prednisone, various anti-seizure medications, and certain barbiturates, or high-dose thyroid replacement drugs.
· Have type 1/ insulin-dependent diabetes, liver disease, kidney disease or a family history of osteoporosis.
· Have high bone turnover, which shows up in the form of excessive collagen in urine samples.
· Have a thyroid or parathyroid condition, such as hyperthyroidism or hyperparathyroidism.